In spite of repeated calls from Ukraine and other countries to the European Union (EU) diplomats and leaders for sanctions against import of Russian natural gas and petroleum oil in relation to Russia's military incursion in Ukraine, there has been no EU consensus yet.
Looking closely, Russia remains the largest supplier of natural gas and petroleum oils to the EU.
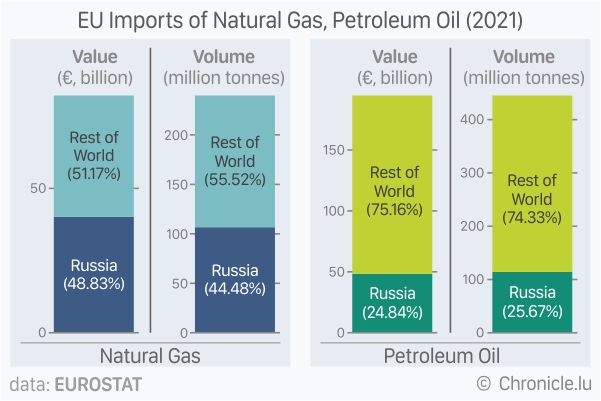
Of the total 239.80 million tonnes equivalent liquefied and gaseous natural gas imported by the EU in 2021, 106.67 million tonnes (44.5%) came from Russia. In terms of value, this represented 48.8% (€40.12 billion) of total trade value of €82.16 billion in 2021.
Moreover, 90.2% (96.18 million tonnes) of the natural gas imported by EU from Russia in 2021 was in gaseous state, mostly through pipelines, and only 9.8% (10.49 million tonnes) in compressed (liquefied) form, making EU imports of Russian gas not only highly dependent due to its high net volume, but also due to infrastructure limitations. For example, even if EU does secure higher volumes of liquefied natural gas from other sources, delivered via sea, it does not have enough capacity and infrastructure to replace the Russian pipeline gas.
The high dependency on Russian gas is also clear with ten out of 27 Member States reporting the national share of Russian gas imports (non-EU partners) was more than 75% by value in 2021. Germany and Italy each had more than 20% share of all the Russian gas imported by EU in 2021.
In comparison, EU was less reliant on Russian petroleum oil imports.
Albeit being the largest trade partner for EU, Russian oil accounted for only 24.8% (€48.36 billion) by value and 25.7% (114.26 million tonnes) by volume, for the total EU oil imports in 2021 totalling €194.68 billion (445.19 million tonnes).
Only four Member States, Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia and Finland, reported their national share of Russian gas imports (non-EU partners) was more than 75% by value in 2021, while the Netherlands accounted for over 20% of all Russian oil imports by EU in 2021.
The European Commission is currently working on the sixth package of EU sanctions against Russia and is expected to exclude Hungary and Slovakia from an embargo on buying Russian oil due to their heavy reliance on Russian oil imports.








