 Credit: STATEC
Credit: STATEC
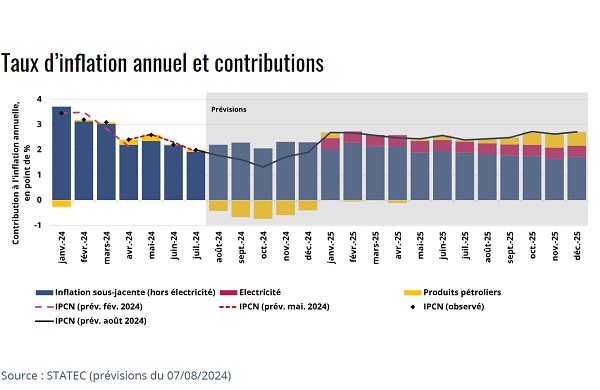
On Wednesday 7 August 2024, Luxembourg’s statistics institute, STATEC, published its updated inflation forecast report.
STATEC maintained its inflation forecast of 2.3% for 2024 but lowered its 2025 estimate to 2.6%.
As STATEC explained, Luxembourg's inflation rate continues to slow down. Inflation is expected to stand at 2.3% this year, with the next wage indexation due in the last quarter. STATEC added that the partial lifting of price caps at the start of 2025 is expected to limit the rise in electricity prices. The statistics institute has thus lowered its inflation forecast for 2025 to 2.6% (previously forecast at 3.1%), with indexation scheduled for the fourth quarter of 2025.
In July 2024, annual inflation in Luxembourg stood at just 2% - the lowest level since the start of 2021. STATEC explained that this decline is the result of the drop in core inflation (2% in July 2024 compared with 4.9% one year earlier), coupled with a slowdown in the price of petroleum products (+1.3% year-on-year in July compared with +4.2% in May). Moreover, the inflation observed over the recent period is close to that anticipated in the forecasts published in May 2024.
The ongoing slowdown in core inflation was helped by the slower rise in food prices and a fall in the prices of non-energy industrial goods (-0.1% year-on-year in July). Food inflation (+1.5% year-on-year) made only a small contribution to overall inflation in July (+0.2 percentage points, compared with +1.3 percentage points a year earlier). Meanwhile, service prices have been slowing for the past two months, rising by 3.5% year-on-year in July (compared with 4.0% in May). STATEC said this mainly reflects the end of the impact of indexation in February and April 2023, adding that only the indexation in September 2023 still had an impact on annual inflation in July.
In the eurozone, on the other hand, inflation is stagnating. STATEC noted that it has hovered around 2.5% since February, reaching 2.6% in July. Services inflation fell slightly to 4% in July (vs +4.1% in June and May), while food inflation was 2.3% (vs +2.4% in June and +2.6% in May).
STATEC also noted that the main international institutions expect inflation in the eurozone to exceed 2% in 2024 and 2025. For 2024, forecasts range from 2.3% (Oxford Economics) to 2.5% (European Commission and ECB). For 2025, inflation is forecast at between 1.4% (Oxford Economics) and 2.2% (ECB and OECD).
The new projections from Oxford Economics (OE), used in STATEC's inflation forecasting model, anticipate a slower decline in consumer prices in the eurozone compared with previous forecasts. This is the result of more sustained momentum in food inflation and energy prices in 2024. OE has revised its inflation forecast for the eurozone to 2.3% in 2024 and 1.4% in 2025 (compared with 2.1% and 1.3% respectively previously). The prices of imported goods, on the other hand, have been revised downwards.
Returning to the situation in Luxembourg, namely regarding the partial removal of energy price cap measures, STATEC said that inflation forecasts now include a limit of 30% on the rise in electricity prices in 2025 (i.e. half of the 60% increase expected in the absence of additional measures), and thus diverge from the unchanged-policy forecast published by STATEC at the beginning of May 2024. Gas prices, for their part, are set to rise by 14%, due to the end of the State's assumption of network costs. This forecast is a direct result of price trends on derivative markets and the way in which energy suppliers in Luxembourg are supplied. STATEC recalled that market price expectations are volatile and that the resulting forecasts for 2025 should be "treated with caution".









