 SDG Star Chart;
Credit: Luxembourg's Ministry of the Environment, Climate and Biodiversity
SDG Star Chart;
Credit: Luxembourg's Ministry of the Environment, Climate and Biodiversity
On Friday 11 April 2025, Luxembourg’s Ministry of the Environment, Climate and Biodiversity presented the National Report "Implementation of the United Nations 2030 Agenda" which had been prepared by the Interdepartmental Commission for Sustainable Development (CIDD) and presents an overview of the ten national priorities defined in the 3rd National Sustainable Development Plan (PNDD).
The 2019 PNDD defined Luxembourg's long-term vision for sustainability. The report details the measures and initiatives implemented by the government in recent years and provides a comprehensive overview of the actions undertaken to achieve the goals set by the 2030 Agenda.
In a press release, the ministry added that the initiatives are complemented by detailed explanations regarding the evolution of the indicators monitored by STATEC, as well as more specific recommendations for progress in sustainability by 2030.
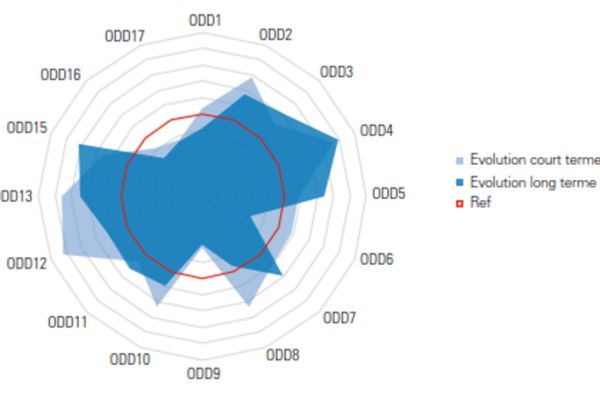
The report is based on 112 indicators, analysed by STATEC, to assess progress on each of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 Agenda. To facilitate the understanding of these results, a visual synthesis method has been developed in the form of a star chart (see image):
The chart shows goals progressing toward sustainability, which are located beyond the red circle, whereas values within the same circle indicate that the goal is moving away from sustainable development. It outlines that the indicators adopted by Luxembourg to measure its progress in achieving the SDGs show progress towards increased sustainability in 70% of the objectives studied.
According to the ministry, Luxembourg is making significant progress regarding SDG 7, related to energy. Energy intensity has been steadily improving since 2004, and the share of renewable energy in total energy consumption is growing exponentially.
SDG 12, dedicated to responsible consumption and production, also shows significant improvement. The green and circular economy is developing in Luxembourg, with a sharp increase in the production of sustainable goods and services, particularly through the construction of passive buildings. The treatment of municipal waste through recycling, composting and energy recovery is steadily increasing, reaching a rate of 93.9% in 2021.
Regarding measures to combat climate change, within the framework of SDG 13, Luxembourg is implementing two complementary approaches: mitigation and adaptation. Mitigation aims to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the country, which decreased by 32.4% in 2021 compared to 2005, a record year for the country. Emissions from sectors not covered by the emissions trading system show a 22.6% reduction since 2005.
SDG 1 on poverty and SDG 6 on water and sanitation show less favourable long-term trends, but the ministry noted that progress has been made over the last five years.
To accelerate progress over the remaining five years to 2030, the report proposes a number of measures, including:
- implementation of the sustainability check: provided for in the National Development Plan (NDP), the sustainability check (Nohaltegkeetscheck) has been in place since 2023. It is an instrument of good governance and support for sustainable development, which provides for a preliminary analysis of the sustainability of legislation. Its consistent use will strengthen policy coherence and improve coordination within the legislative framework;
- supporting and promoting municipalities: municipalities are key players in sustainable development. Through their involvement in initiatives such as the Climate, Nature and Housing Pacts, and the Citizens' Pact for Intercultural Living Together, they directly contribute to the implementation of the SDGs on the ground;
- supporting businesses: the transition to greater sustainability requires increased support for businesses, particularly in the areas of decarbonisation and innovation. Their participation is essential to achieving the objectives set by 2030 - each within its own means;
- developing a roadmap: the report recommends the establishment of a roadmap for sustainable development. This would bring together several areas and policies under common "entry points" to facilitate progress toward national priorities and the SDGs of the 2030 Agenda.








