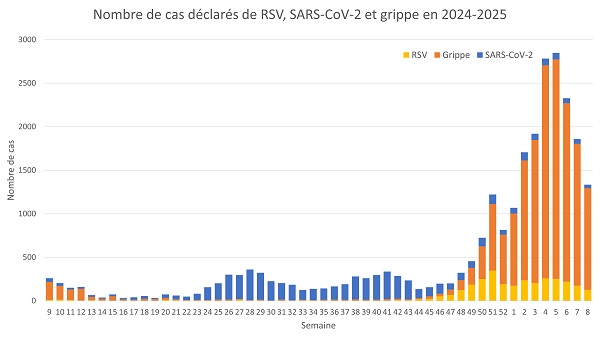
 Number of reported cases of RSV, flu and COVID-19 in 2024-2025;
Credit: MSSS
Number of reported cases of RSV, flu and COVID-19 in 2024-2025;
Credit: MSSS
On Thursday 27 February 2025, the Health Directorate of Luxembourg's Ministry of Health and Social Security published its weekly retrospective concerning the evolution of the main acute respiratory infections including COVID-19, influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
From Monday 17 to Sunday 23 February 2025, the number of influenza (flu) cases reported by laboratories decreased from 1,630 to 1,166, down 28% compared to the previous week. Infections remained common among children. The health authorities said the drop in the number of cases observed over the past three weeks confirms that the peak of the epidemic is over.
During the week in question, there were 38% influenza A and 62% influenza B among the typed results. According to the latest available data, the subtypes identified among the influenza A virus samples were A(H1)pdm9 (44.1%) and A(H3) (55.9%).
The health authorities reiterated the importance of adopting barrier gestures, as well as getting vaccinated, to limit the spread of the seasonal flu:
- wash hands regularly with soap and water for 30 seconds, carefully rubbing the palms, fingers, backs of hands and under the nails;
- cover one's mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. If a tissue is not available, use the crook of the elbow;
- immediately throw used tissues in the bin and then wash one's hands;
- avoid physical contact such as hugs, kisses and handshakes;
- avoid crowds and gatherings during the epidemic season;
- stay home if sick, to avoid contaminating others;
- ventilate rooms regularly, at least three to four times a day for ten minutes.
Regarding RSV, the number of reported cases decreased by 27%, with 127 confirmed cases, compared to 174 the previous week. Infections mainly affected very young children and older people (aged 80+).
The health authorities also noted a decrease in the number of cases of COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2, from 55 to 42. This represents a decline of 24% over one week. The viral concentration detected in wastewater also showed a decrease.
The latest available sequencing data revealed that two sub-variants of JN.1, the XEC variant (47.7%) and the KP.3 variant (22.1%), predominated in January 2025.









